salt: know the benefits of this food seasoning
salt: health benefits and delicious recipes, Salt has become an inseparable part of human life. Salt is usually used as one of the main spices to add flavor to food.
 |
| salt: health benefits and delicious recipes |
Besides being mixed in food, salt is also often served at the dining table as a complement or condiment with pepper.
type salt today is also diverse. There are table salt, Himalayan salt, to sea salt. Salt, in sufficient quantities is needed to maintain fluid balance in the body and plays a role in maintaining muscle and muscle function. However, diseases will arise due to excess salt, ranging from nervous disorders, cancer, to heart disease.
Without salt, every dish you make will taste different. The existence of this spice cannot be ignored.
However, there are many types of salt with varying characters. Some are easy to mix with food without having to heat it, some are so hard that if you are not careful, the salty taste of the dishes is uneven.
Even though they are both salty, each type of salt has a different designation. From table salt to kosher salt, here are the differences and uses.
1.Table salt (iodized salt)
Table salt or commonly called iodized salt is most often found in households. The texture is very smooth, much smoother than granulated sugar. Quoting Healthline, this fine texture is obtained from a heavy grinding process that removes most of the impurities and minerals in it.
Nearly pure table salt contains sodium chloride (about 97 percent or higher). In many countries, table salt contains added iodine.
This type of salt is also often one of the health steps to overcome the problem of iodine deficiency. Iodine deficiency can lead to hypothyroidism (thyroid hormone deficiency), intellectual disabilities, and other health problems.
2.Krosok salt (coarse salt)
Krosok salt has a larger and coarser grain than table salt. Salt has a much stronger salty taste and doesn't dissolve easily. Generally, krosok salt is used to preserve fish, salted fish production, as well as a mixture of animal feed.
If broken down, krosok salt can be used for cooking. Chef Amy Eubanks said salt can be used as a topping at the end of processing, but not as a spice. "This salt is more [suitable] for the end or garnish," Eubanks quoted Self as saying.
3. Sea salt (sea salt)
As the name suggests, sea salt is made through the evaporation process (evaporation) of seawater. The mineral content contained will vary depending on the origin of the sea. Generally, sea salt contains minerals such as potassium, iron and zinc. The darker the color, the higher the concentration of minerals and pollutants.
Sea salt looks like a crystal flake and is scaly. Once sprinkled, the salt will spread out evenly and leave no explosion of salty taste.
4.Himalayan salt (Himalayan pink salt)
Himalayan salt or often called Himalayan pink salt is salt obtained from the Khewra salt mine, Pakistan. It is the second largest salt mine in the world after Golderich in Canada. The pink color is obtained from the content of iron oxide (iron oxide).
Compared to regular table salt, the sodium content of Himalayan salt is somewhat lower. If table salt is 39.1 percent sodium, Himalayan salt is about 36.8 percent.
This salt contains a small amount of calcium, iron, potassium and magnesium. This mineral content also makes Himalayan salt more desirable.
According to Eubanks, this added mineral also makes the taste of Himalayan salt somewhat different from other salts. You will get a slightly different presentation of taste when you add salt as the final touch to the dish.
5.Kosher salt
Kosher salt is popular in North America. Usually kosher salt is used for the 'koshering salt' process, which is to remove blood from the meat including rinsing, soaking, and salting.
"Many professional kitchen workers use kosher salt because of its low salinity which doesn't make dishes salty. Its large, coarse-like shape makes it easy to pick up and spread with your fingers," explains Eubanks.
This type of salt, he said, is best for salting meat.
What are the benefits of salt for health?
Prevent Goiter. The content of salt can prevent goiter, Maintain Electrolyte Balance, Prevent Hyponatremia, Maintain Oral Health, Maintain Digestive Health, Prevent Low IQ. Role in the Nervous System.
1. Preventing Goiter
The salt content can prevent goiter. How come? Without an adequate amount of iodine, the thyroid gland will swell due to the body's demand to continue producing thyroid hormones. Swelling of the thyroid gland results in a change in the shape of the neck in which the neck will swell or a lump will appear.
In addition, the body needs thyroid hormone for the development of the brain and spinal structures in the early development of children. If pregnant or breastfeeding women are deficient in iodine, mental retardation in children can occur.
2. Maintain Electrolyte Balance
This benefit of salt for the body is very important, because it can maintain hydration levels. Especially for people who work outdoors and who exercise regularly, they need to recover from the lack of salt and water that occurs through sweating.
If the electrolyte balance in the body is maintained properly, the function of human organs can also run well.
3. Dispels Hyponatremia
Hyponatremia is a condition in which the body suffers from a lack of salt in the body cell fluids. Usually the fluid will come out in the form of sweat, diarrhea, or what is commonly known as water intoxication.
To maintain healthy blood pressure and smooth function of nerves and muscles, the body craves salt. If the need for salt is not fulfilled, there will be an imbalance in the water content in the body and eventually swelling because the cells are excess water.
4. Maintaining Oral Health
One of the properties of salt is to maintain oral health. You need to know that bacterial infections of the mouth can cause problems with teeth and gums.
To prevent bacteria from growing, gargle with salt water. This is believed to reduce swelling and relieve pain in the gums.
5. Maintain Digestive Health
The next benefit of salt is that it helps maintain digestive health. If you are on a diet and there is not enough salt in your body, the effects will be very dangerous. The body will not produce enough HCl (hydrochloric acid) in the stomach.
This condition will get worse if you previously have a history of poor digestive health, such as stomach acid. With enough salt, the body will prevent stomach acid from rising up into the throat. So for those of you who have digestive problems, the use of salt actually plays an important role for you.
6. Prevent low IQ
Iodine is very important in brain development, especially at the age of 3-5 years. According to research, those who lack iodized salt tend to have a lower IQ than those whose iodine needs are well met.
7. Role in the Nervous System
As a provider of sodium, salt is not only good for the brain, but also muscles and nervous system function. Sodium is a regulator of water in your body. This is necessary for the transmission of electrical signals in the body.
The Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia advises adults to limit salt consumption per day to 2,000 milligrams (mg). This amount is approximately 1 teaspoon.
Eating too much salt will make the body retain more fluid which has an impact on the work of blood vessels. The result can be high blood pressure, stroke, kidney problems and affect the work of the heart in the future.
some of the health benefits of salt that you can get. But remember, consume in moderation according to recommendations to get health benefits. Conversely, if excessive, it will actually trigger various diseases in your body.
What is the impact of iodine deficiency on children?
Iodine deficiency during pregnancy can cause the child to develop cretinism (congenital or congenital hypothyroidism). Cretinism in children can cause developmental disorders, such as muscle tension, stunting, gait problems, deafness, and speechlessness.
The body must be avoided from iodine deficiency because the body needs a certain amount of iodine. Its function is to be able to produce adequate thyroid hormones.
Even though it requires iodine, the body doesn't produce it naturally. The way to get these nutrients is through food. Adults generally need about 150 micrograms of iodine per day. Pregnant and breastfeeding women need about 20 micrograms of iodine per day.
Iodine can be found in various types of food. Starting from fish, eggs, nuts, meat, bread, milk and processed products, seaweed, and iodized salt.
About two billion people worldwide are deficient in iodine. This is especially true in developing countries, where many people have limited access to healthy food. However, this condition can also affect anyone, even those in developed countries, who are not getting enough iodine intake or their body is unable to process iodine properly.
It should also be noted that pregnant women need more iodine intake. Therefore, intake of foods with high iodine levels is especially recommended for this group.
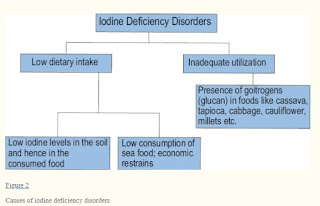
Causes of iodine deficiency
Iodine deficiency is caused by insufficient iodine intake for daily needs. Lack of iodine intake causes a decrease in thyroid hormone production, which in turn leads to enlargement of the thyroid gland.
Symptoms of iodine deficiency
Signs and symptoms of iodine deficiency can include:
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland in the neck, which is characterized by a lump that appears on the neck
- Fatigue
- Increased sensitivity to cold temperatures
- Constipation
- Dry skin
- Increase in weight
- Swollen face
- Muscle weakness
- Increased cholesterol levels in the blood
- Pain or stiffness in muscles and joints
- Decreased heart rate
- Thinning hair
- Depression
- Memory weakness
- Menstruation with excessive bleeding in women
- In infants, hypothyroidism can cause signs and symptoms that include:
- Choking frequently
- Enlargement of the tongue
- Swollen face
- Constipation
- Weak muscle mobility
- Excessive sleepiness
- In children and adolescents, hypothyroidism can cause signs and symptoms that include:
- Poor growth
- Delays in tooth development
- Delayed puberty
- Poor mental development
- In addition, this condition can also cause cognitive problems such as low intelligence quotient (IQ), learning difficulties, and mental disabilities (especially in children).
Diagnosis of Iodine Deficiency
If the doctor suspects that there is a deficiency or deficiency of iodine, several investigations can be done to detect iodine levels in the body, including:
Urine examination.
This examination is the simplest, fastest way, and the results can be found in a matter of minutes. However, the results obtained may not be as accurate as other iodine tests.
Blood check.
This simple and accurate test is performed to check the iodine levels in the body. It can take longer than the urine test to find the results.
Iodine patch check.
This examination is done by placing an iodine patch on the skin and examining it 24 hours later.
In those without iodine deficiency, the iodine patch will start to disappear after 24 hours. However, those with iodine deficiency will lose the iodine patch more rapidly. However, these checks are not always accurate.
Iodine loading check.
This test measures the amount of iodine excreted in the urine over a 24 hour period. Although it is not a quick or easy examination to perform, it is considered quite accurate.
Management of iodine deficiency
Iodine deficiency can be corrected by having a healthy diet and rich in iodine. If dietary changes are not sufficient for iodine needs, your doctor may consider giving iodine supplements.
People who generally do not get adequate amounts of iodine from their daily diet are those who are on a vegetarian, vegan, or pregnant woman diet. Iodine supplements that contain potassium are the most easily absorbed by the body.
Prevention of iodine deficiency
Iodine deficiency can be prevented by ensuring adequate iodine intake every day. The Institute of Medicine recommends a recommended daily intake of 150 micrograms of iodine per day for women and men, 220 micrograms per day for pregnant women, and 290 micrograms per day for breastfeeding women. One teaspoon of iodized salt contains about 400 micrograms of iodine.
Even though it is only needed in small amounts, the fact is that many people experience a deficiency in this mineral intake. The various signs and symptoms of iodine deficiency include:
If the body does not get the iodine intake it needs in a day, the body will be susceptible to disorders due to iodine deficiency (GAKI). These include goiter, hypothyroidism, mental retardation, miscarriage, and physical development problems.
how do you know the symptoms of an iodine deficiency in the body?
1. Swelling of the thyroid gland
When your iodine intake is less than 100 mcg (micrograms) per day, your body will start overproducing thyroid hormone (TSH). This can lead to swelling of the thyroid gland, also known as a goiter.
In Indonesia, this condition is better known as goiter. You may think that a goiter lump can be clearly visible on the neck and is painful. Even though it's not the case, you know.
An assistant lecturer in endocrinology and metabolism from the Comprehensive Cancer Center at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center, Brittany Henderson, MD, said that goiter can only be seen through ultrasound or CT scan.
However, if you experience a lump in your throat such as when you are choking or have difficulty swallowing, then this could be an early symptom of goiter.
2. Weight gain dramatically
if you feel that you have gained a lot of weight even though you are not eating much, you could be short on iodine. However, not all cases of weight gain are definite symptoms of iodine deficiency.
The main function of the thyroid hormone is to help control the body's metabolism by breaking down food into energy and heat. When the thyroid hormone levels are low, the body will be overwhelmed to process food. As a result, calories from food will be stored in the form of fat and increase your weight.
3. Easily tired and cold
Naturally, if the body feels tired after a day of activities. But be careful, this can also be one of the symptoms of iodine deficiency.
A study published in the journal Hippokratia in 2010 revealed that about 80 percent of people with low thyroid levels are prone to fatigue and cold easily. The reason is, the body's slow metabolism makes the body fail to produce energy. The body feels weak and gets cold easily.
4. Hair loss and dry skin
Not only regulates the body's metabolism, thyroid hormone also functions to control hair follicle growth. When the body's thyroid hormones are low, your hair follicles will stop regenerating, aka growing back. This is what makes hair thin and easy to fall out.
Not only hair, cell regeneration also depends on the level of thyroid hormone in the body. Skin cells will find it difficult to regenerate and sweat less frequently when the body is getting less iodine intake. As a result, the skin tends to be dry and peels easily.
5. Heart rate slows down
Sooner or later your heart rate is influenced by the iodine content in the body. If the level of this mineral is too low, your heart rate will decrease. Vice versa, most iodine intake can increase heart rate.
Iodine deficiency is severe and chronic can cause your heart rate to slow down abnormally. If not addressed, this can cause the body to feel weak, tired, dizzy, and even fainting.
6. Difficulty remembering
A study involving 1,000 adults found that participants with high thyroid hormone levels tended to have strong and perceptive memories, compared to participants with low thyroid hormone levels.
Thyroid hormone also plays an important role in brain growth and development. Experts found that the size of the hippocampus, the part of the brain that controls long-term memory, tends to be smaller in people with low thyroid levels. That is why, lack of iodine can inhibit brain development and make it easy for you to forget.
More Information: www.foodnusantara.eu.org